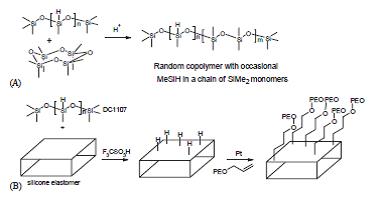
Protein repellant silicone surfaces by covalent immobilization of poly(ethylene oxide)
Biomaterials,
2005,
26,
2391-2399.
文章链接:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.07.068
Protein repellant silicone surfaces by covalent immobilization of poly(ethylene oxide)
发布日期:2005-12-25
Polydimethylsiloxane elastomers were surface modified with passivating polyethylene oxide (PEO) polymers of different molecular weights, both monoftinctional and bifunctional. Following the introduction of Si-H groups on the surfaces by acid catalysed equilibration in the presence of polymethylhydrosiloxane, the PEO was linked by platinum-catalyzed hydrosilylation. ATR-FTIR, X-ray photoetectron spectroscopy (XPS) and water contact angle results confirmed that the PEO was successfully grafted to the silicone rubber. Atomic force microscopy and XPS suggested that surface coverage with PEO was very high on the modified surfaces but not complete. The protein-resistant properties of the PEO-modified surfaces were demonstrated by measuring he adsorption of fibrinogen from both buffer and plasma. Fibrinogen adsorption from buffer to the PEO-modified surfaces was reduced by more than 90% compared with controls.