Tissue plasminogen activator-containing polyurethane surfaces for fibrinolytic activity
Acta Biomaterialia,
2011,
7,
1993-1998.
文章链接:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2011.01.026
武照强老师在Acta Biomaterialia上发表研究论文
发布日期:2011-09-08
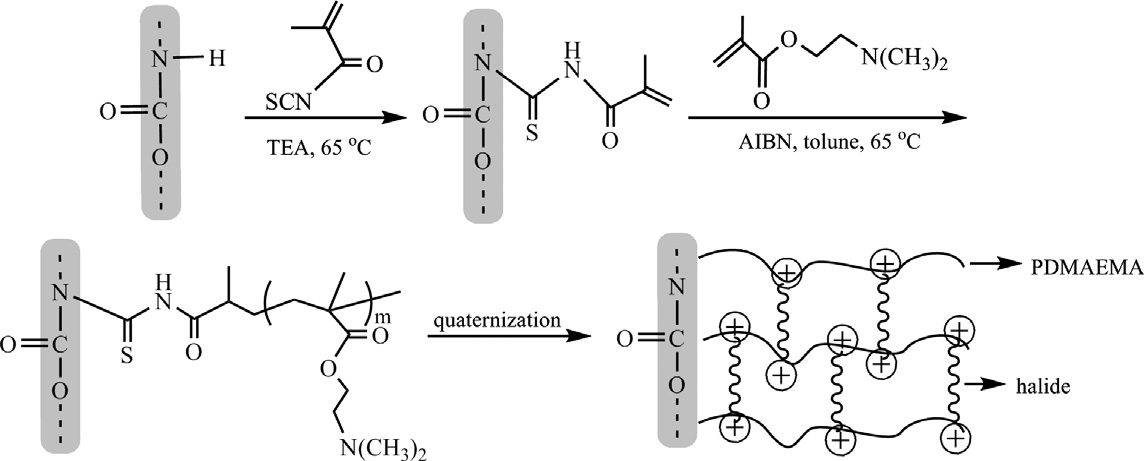
With the aim of minimizing thrombus formation in blood-contacting devices, tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA)-containing polyurethane (PU) materials have been developed. Cationic PU surfaces were prepared by grafting poly(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) and quaternizing the tertiary amino groups with iodomethane or 1,6-diiodohexane or a,a0-dichloro-p-xylene. The surfaces were characterized by water contact angles and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The materials (PU-CH3I, PU-I(CH2)6I, PUCl) were treated with t-PA in Tris-buffered saline (pH 9.0) to give t-PA-loaded PU surfaces. The t-PA content of the surfaces was determined using radiolabeled t-PA. The quantities of t-PA taken up by the cationic surfaces were significantly greater than on the unmodified PU: approximately 14-fold greater for PU-Cl, 10-fold for PU-CH3I and 13-fold for PU-I(CH2)6I. The activity of the bound t-PA, as measured by a plasma clotting–dissolution assay and a chromogenic substrate assay, was similar to that of normal, unbound t-PA. Release of t-PA from these materials in contact with plasma was measured using the labeled protein and was found to be the most rapid on the PU-CH3I material. This approach may have potential for the development of surfaces which can lyse clots that begin to form on them