Spectroscopic investigation of the interactions between gold nanoparticles and bovine serum albumin
Chinese Science Bulletin,
2012,
57,
1109-1115.
文章链接:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4741-3
石秀娟同学在Chinese Science Bulletin发表研究论文
发布日期:2012-06-08
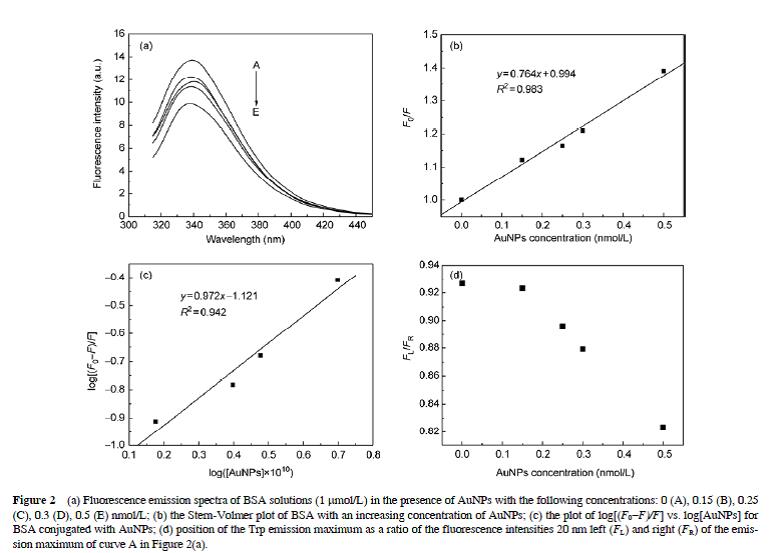
The interactions between bovine serum albumin (BSA) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), and the conformational changes of BSA induced by this interaction, were investigated by UV-visible absorption spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, and Fourier transform infrared in combination with attenuated total reflection spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR). The critical adsorption density for preventing AuNP aggregation in 0.1 mol/L phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.2) was 23 BSA molecules per gold particle or 3.8×1012 BSA molecules/cm2. BSA bound to the AuNPs with high affinity (binding constant Ks=7.59×108 L/mol), and the intrinsic fluorescence of BSA was quenched by the AuNPs in accordance with the static quenching mechanism. Both fluorescence spectroscopy and ATR-FTIR showed that AuNPs induced conformational changes in BSA, which resulted in it becoming less compact and increased the polarity of the microenvironment around the tryptophan residue Trp-212.