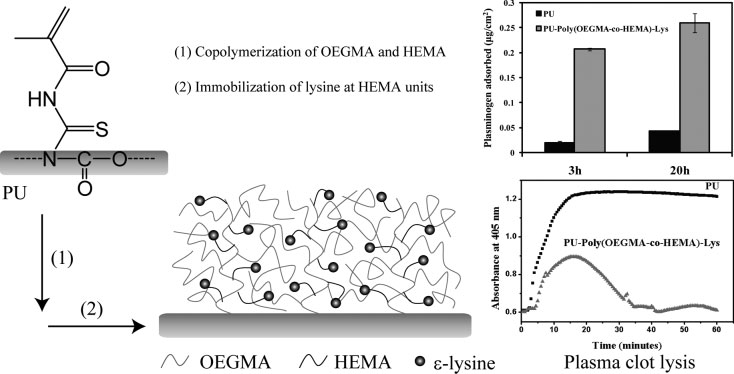
Protein-resistant and fibrinolytic polyurethane surfaces
Macromolecular Bioscience,
2012,
12,
126-131.
文章链接:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201100211
武照强副教授在Macromolecular Bioscience发表研究论文
发布日期:2012-09-08
Surfaces with resistance to non-specific protein adsorption and a high capacity to bind plasminogen from plasma are developed for application as fibrinolytic surfaces in blood contact. A new method is reported for grafting poly(OEGMA-co-HEMA) copolymers on polyurethane surfaces. The OEGMA provides effective protein resistance due to the PEG side chains and the HEMA provides a high density of OH groups for attachment of lysine. Adsorption of fibrinogen from buffer and plasma to these surfaces is low, indicating significant protein resistance. Plasminogen binding from plasma is high, and clot dissolution on surfaces where plasminogen adsorbed from plasma is converted to plasmin is rapid.